The students start to learn mathematics problem solving with simple one operations like subtraction/ multiplication/ addition/ division. These single operations are very simple to do but what about problems containing more than one operation like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division in the same problem? This is where the BODMAS Rule plays a vital role in solving these types of problems with 100% accuracy.
What is the BODMAS Rule?
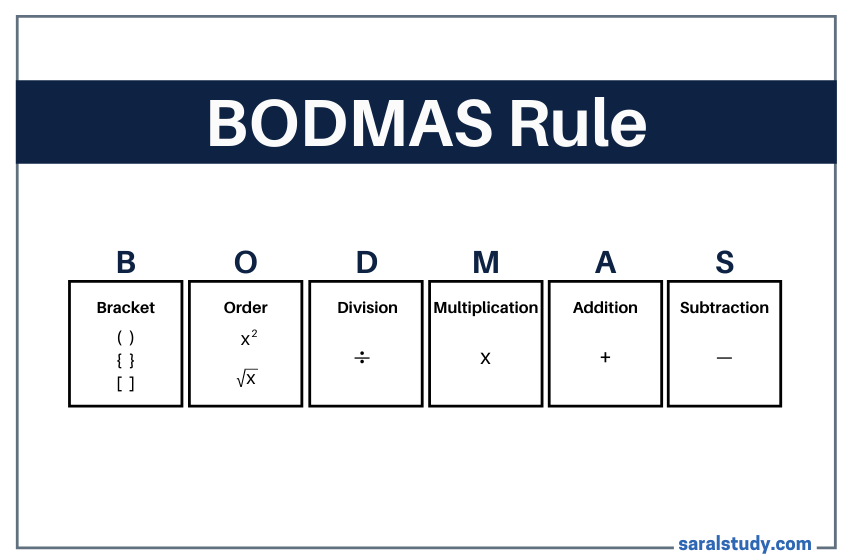
The BODMAS rule is a trick to solve primary school mathematical questions which stands for
- B – Bracket
- O – Orders (i.e., powers and square roots, etc.)
- D – Division
- M – Multiplication
- A – Addition
- S – Subtraction
BODMAS helps students remember the order of operations to follow when solving a mathematical expression. In some regions, it’s referred to as BIDMAS (where ‘I’ stands for Indices) or PEMDAS in the USA (where ‘P’ stands for Parentheses and ‘E’ for Exponents)..
In some places like the USA, it is also known as PEMDAS
- P – Parentheses
- E – Exponents
- M – Multiplication
- D – Division
- A – Addition
- S – Subtraction.
Order of operations of BODMAS Rule
Mathematics relies on a universal set of rules to determine the sequence of operations. The BODMAS rule establishes this order:
- Brackets: Solve expressions inside brackets first.
- Orders: Solve exponents (orders and indices) next.
- Division: Solve division then
- Multiplication: Solve multiplication, and then
- Addition and Subtraction: Finally, solve the addition followed by subtraction.
Understanding and applying BODMAS ensures that complex mathematical expressions are solved correctly and consistently.
BODMAS FULL FORM
BODMAS stands for Brackets, Orders, Division, Multiplication, Addition, and Subtraction. It is a mathematical acronym that represents the order in which arithmetic operations should be performed to solve an expression.
Explanation:
- Brackets: Solve anything inside brackets first.
- Orders: Handle powers and roots (such as squares, cubes, and square roots).
- Division and Multiplication: Perform from left to right.
- Addition and Subtraction: Finally, perform addition and subtraction from left to right.
Using BODMAS helps avoid confusion and ensures accurate calculation of complex mathematical expressions.
History and Importance of BODMAS Rule
The precedence rules in mathematics have evolved over centuries. Multiplication and division were given higher precedence than addition and subtraction since the introduction of modern algebra. Exponents were introduced in the 16th and 17th centuries, adding another layer to the order of operations. BODMAS was established to provide a clear framework for solving expressions with multiple operations.
Order of operation according to BODMAS Rule
B O D M A S Bracket () Order √ Division ÷ Multiplication x Addition + Subtraction -
Examples of BODMAS Rule
Example 1: 4 + 2 x 8 =?
Solution: According to the BODMAS Rule, Multiplication needs to be done before addition.
So,
Step 1: 2 x 8 = 16
Step 2: 4 + 16 = 20
The correct answer is 20.
(Common mistake that students make: 4 + 2 = 6, 6 x 8 = 48)
Example 2: 6 – 3 + 8 ÷ 2 =?
Solution: Applying BODMAS Rule,
Step 1: 8 ÷ 2 = 4
Step 2: Mow, We have 6 – 3 + 4
So, 6 – 3 = 3
Step 3: + 4 = 7
7 is the correct answer
(Common errors: 6 – 3 = 3, 3 + 8 = 11, 11 ÷ 2 = 5.5)
Example 3: 4 x (5 + 6) + 5 2 =?
Solution: Apply BODMAS Rule,
Step 1: (5 + 6) = 11
Step 2: 5 2 = 25
Step 3: 4 x 11 = 44
Step 4: 44 + 25 = 69
69 is the correct answer
(Common errors: many students work from left to right and get wrong answer)
Example 4: Find the value of z using BODMAS Rule 33 ÷ 3 + z x 3 -23 = 0
Solution: Apply BODMAS Rule,
Step 1: 33 ÷ 3 = 11
Step 2: z x 3 = 3z
Step 3: now, we have 11 + 3z -23 = 0
Step 4: 11 + 3z = 23
Step 5: 3z = 23 – 11
Step 6: 3z = 12
Step 7: z = 12 ÷ 3
Step 8: z = 4
The value of z is 4.
Example 5: (6÷4+2÷4) -2 =?
Solution: Applying BODMAS Rule
Step 1: (6/4+2/4) = 2
Step 2: 2 – 2 = 0
0 is the correct answer
Example 6: 3×3-3÷3+3
solutions: Applying BODMAS Rule
Step 1: 3 ÷ 3 = 1
Step 2: 3 x 3 = 9
Step 3: now, we have 9-1+3
Step 4: 9 + 3 = 12
Step 5: now, we have 12-1
Step 6: 12-1=11
The correct answer is: 11
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the need of the BODMAS Rule?
Ans. The BODMAS helps students to solve the mathematical problem in the proper order of operations. When students reach the primary classes, they need to solve mathematical problems that require more than one operation. These kinds of problems have more chances of mistakes, BODMAS plays an important role here in eliminating confusion and errors while solving the problem.
BODMAS instructs that brackets should be solved first, then comes the orders, followed by the division or multiplication and addition or subtraction at the last. It is the most useful rule to make difficult expressions easy to understand. BODMAS is a very easy and simple rule which can be understood easily by the students in primary classes.
Q2. Please give an example of the BODMAS Rule.
Ans. Here is the BODMAS rule example:
4 + 3 x 8 =?
Solution: According to the BODMAS rule, Multiplication needs to be done before addition.
So,
Step 1: 3 x 8 = 24
Step 2: 24 + 4 = 28
The correct answer is 20.
(Common mistake that students make: 4 + 3 = 7, 7 x 8 = 56)
You can find more examples above in the article.
The BODMAS rule is the order of the operations used in solving algebraic problems. First, start with solving the brackets, then orders followed by division and multiplication and addition/subtraction are the last step. If students fail to use the rule properly or ignore the BODMAS rule while solving the question, they will get the wrong answer.
Q3. What is the full form of BODMAS?
Ans. The full form of BODMAS is :
B- Brackets () / {} / []
O- Orders (powers and roots, √)
D- Division (÷)
M- Multiplication (x)
A – Addition (+)
S- Subtraction (-)
Q4. Are BODMAS and PEMDAS the same?
Ans. BODMAS and PEMDAS are exactly the same things. PEMDAS is usually used in the UK. Although PEMDAS indicates to do multiplication before division but that doesn’t change the calculation. Either way, the answer will be the same.
For example: 5 ÷ 2 x 3 = 7.5 and 5 x 3 ÷ 2 = 7.5. In both cases the answer is same.
Q5. Are Orders, Indices and Exponents the same?
Ans. Orders, Indices, and exponents are the same things which are the subscript numbers representing the powers in Mathematics. These are the half-size numbers we usually see in algebraic expressions as powers. For example: 3 2 +5, Here, 2 is the power of 3. This can be denoted as order, index, or exponent.
Q6. Is BODMAS a universal rule?
Ans. Yes BODMAS is a universal rule. It was introduced by Achilles Reselfelt. This was introduced to make it easy to solve mathematical problems involving more than one sign or operation. BODMAS tells us the order in which we have to operate.
BODMAS was created according to the rule of mathematics and the precedence of one operation over another. As it is not easy to remember all the rules and precedence, BODMAS is a simple way to solve them. This is accepted universally. Some places call it PEMDAS or BIDMAS also but they are all the same things.
Q7. Is there any chance of getting the wrong answer after using BODMAS?
Ans. Although BODMAS is the rule to solve problems involving multiple operations but the correct calculations and using it properly is the responsibility of students. If you use the BODMAS rule correctly and make no mistakes in calculations, you will surely get the right answer.
Also Read: Vedic Mathematics: History, Tricks, Techniques and Example