Class 12 Chemistry - Chapter Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids NCERT Solutions | How will you convert ethanal into the fo
How will you convert ethanal into the following compounds?
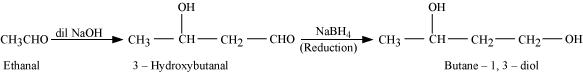
(i) Butane-1, 3-diol (ii) But-2-enal (iii) But-2-enoic acid
(i) On treatment with dilute alkali, ethanal produces 3-hydroxybutanal gives butane-1, 3-diol on reduction.
(ii) On treatment with dilute alkali, ethanal gives 3-hydroxybutanal which on heating produces but-2-enal.

(iii) When treated with Tollen's reagent, But-2-enal produced in the above reaction produces but-2-enoic acid .

More Questions From Class 12 Chemistry - Chapter Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Q:-
Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds.
(i) Propanal and Propanone
(ii) Acetophenone and Benzophenone
(iii) Phenol and Benzoic acid
(iv) Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate
(v) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one
(vi) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone
(vii) Ethanal and Propanal
- Q:-
Which of the following compounds would undergo aldol condensation, which the Cannizzaro reaction and which neither? Write the structures of the expected products of aldol condensation and Cannizzaro reaction.
(i) Methanal (ii) 2-Methylpentanal
(iii) Benzaldehyde (iv) Benzophenone
(v) Cyclohexanone (vi) 1-Phenylpropanone
(vii) Phenylacetaldehyde (viii) Butan-1-ol
(ix) 2, 2-Dimethylbutanal
- Q:-
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions.
(i)Ethanal, Propanal, Propanone, Butanone.
(ii)Benzaldehyde, p-Tolualdehyde, p-Nitrobenzaldehyde, Acetophenone.
Hint:Consider steric effect and electronic effect.
- Q:-
Write the structures of the following compounds.
(i) α-Methoxypropionaldehyde
(ii) 3-Hydroxybutanal
(iii) 2-Hydroxycyclopentane carbaldehyde
(iv) 4-Oxopentanal
(v) Di-sec-butyl ketone
(vi) 4-Fluoroacetophenone
- Q:-
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated:
(i) Acetaldehyde, Acetone, Di-tert-butyl ketone, Methyl tert-butyl ketone (reactivity towards HCN)
(ii) CH3CH2CH(Br)COOH, CH3CH(Br)CH2COOH, (CH3)2CHCOOH, CH3CH2CH2COOH (acid strength)
(iii) Benzoic acid, 4-Nitrobenzoic acid, 3,4-Dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-Methoxybenzoic acid (acid strength)
- Q:-
Describe the following:
(i) Acetylation
(ii) Cannizzaro reaction
(iii) Cross aldol condensation
(iv) Decarboxylation
- Q:-
Give plausible explanation for each of the following:
(i) Cyclohexanone forms cyanohydrin in good yield but 2, 2, 6 trimethylcyclohexanone does not.
(ii) There are two -NH2 groups in semicarbazide. However, only one is involved in the formation of semicarbazones.
(iii) During the preparation of esters from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst, the water or the ester should be removed as soon as it is formed.
- Q:-
Which acid of each pair shown here would you expect to be stronger?
(i) CH3CO2H or CH2FCO2H
(ii)CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
(iii) CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
(iv)

- Q:-
Predict the products formed when cyclohexanecarbaldehyde reacts with following reagents.
(i) PhMgBr and then H3O+
(ii)Tollens' reagent
(iii) Semicarbazide and weak acid
(iv)Excess ethanol and acid
(v) Zinc amalgam and dilute hydrochloric acid
- Q:-
Predict the products of the following reactions:
(i)

(ii)

(iii)

(iv)

Popular Questions of Class 12 Chemistry
- Q:-
For the reaction R → P, the concentration of a reactant changes from 0.03 M to 0.02 M in 25 minutes. Calculate the average rate of reaction using units of time both in minutes and seconds.
- Q:-
Write the formulas for the following coordination compounds:
(i) Tetraamminediaquacobalt (III) chloride
(ii) Potassium tetracyanonickelate(II)
(iii) Tris(ethane-1,2-diamine) chromium(III) chloride
(iv) Amminebromidochloridonitrito-N-platinate(II)
(v) Dichloridobis(ethane-1,2-diamine)platinum(IV) nitrate
(vi) Iron(III) hexacyanoferrate(II)
- Q:-
(i) Write structures of different isomeric amines corresponding to the molecular formula, C4H11N
(ii) Write IUPAC names of all the isomers.
(iii) What type of isomerism is exhibited by different pairs of amines?
- Q:-
Why are solids rigid?
- Q:-
Write any two characteristics of Chemisorption.
- Q:-
Which of the ores mentioned in Table 6.1 can be concentrated by magnetic separation method?
- Q:-
Why are pentahalides more covalent than trihalides?
- Q:-
Silver atom has completely filled d orbitals (4d10) in its ground state. How can you say that it is a transition element?
- Q:-
Glucose or sucrose are soluble in water but cyclohexane or benzene (simple six membered ring compounds) are insoluble in water. Explain.
- Q:-
Write structures of the following compounds:
(i) 2-Chloro-3-methylpentane
(ii) 1-Chloro-4-ethylcyclohexane
(iii) 4-tert. Butyl-3-iodoheptane
(iv) 1,4-Dibromobut-2-ene
(v) 1-Bromo-4-sec. butyl-2-methylbenzene
Recently Viewed Questions of Class 12 Chemistry
- Q:-
Write the chemistry of recharging the lead storage battery, highlighting all the materials that are involved during recharging.
- Q:-
How is 'cast iron' different from 'pig iron"?
- Q:-
Vapour pressure of pure water at 298 K is 23.8 mm Hg. 50 g of urea (NH2CONH2) is dissolved in 850 g of water. Calculate the vapour pressure of water for this solution and its relative lowering.
- Q:-
How will you bring about the following conversions?
(i) Ethanol to but-1-yne
(ii) Ethane to bromoethene
(iii) Propene to 1-nitropropane
(iv) Toluene to benzyl alcohol
(v) Propene to propyne
(vi) Ethanol to ethyl fluoride
(vii) Bromomethane to propanone
(viii) But-1-ene to but-2-ene
(ix) 1-Chlorobutane to n-octane
(x) Benzene to biphenyl.
- Q:-
How is dacron obtained from ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid?
- Q:-
Write any two characteristics of Chemisorption.
- Q:-
How will you convert:
(i) Ethanoic acid into methanamine
(ii) Hexanenitrile into 1-aminopentane
(iii) Methanol to ethanoic acid
(iv) Ethanamine into methanamine
(v) Ethanoic acid into propanoic acid
(vi) Methanamine into ethanamine
(vii) Nitromethane into dimethylamine
(viii) Propanoic acid into ethanoic acid
- Q:-
How will you convert?
(i) Benzene into aniline
(ii) Benzene into N, N-dimethylaniline
(iii) Cl-(CH2)4-Cl into hexan-1, 6-diamine?
- Q:-
What is the effect of temperature on the rate constant of a reaction? How can this temperature effect on rate constant be represented quantitatively?
- Q:-
Write reactions of the final alkylation product of aniline with excess of methyl iodide in the presence of sodium carbonate solution.
4 Comment(s) on this Question
Pokor kela pokor. Nice. Easily understood. Greatly helpful.
Good
It is really helpful
Thanks, it has been really helpful
- All Chapters Of Class 12 Chemistry
- All Subjects Of Class 12
