Class 12 Chemistry - Chapter Alcohols Phenols and Ethers NCERT Solutions | Explain the fact that in aryl alkyl ethe
Explain the fact that in aryl alkyl ethers
(i) The alkoxy group activates the benzene ring towards electrophilic substitution and
(ii) It directs the incoming substituents to ortho and para positions in benzene ring.
(i)

In aryl alkyl ethers, due to the +R effect of the alkoxy group, the electron density in the benzene ring increases as shown in the following resonance structure.

Thus, benzene is activated towards electrophilic substitution by the alkoxy group.
(ii) It can also be observed from the resonance structures that the electron density increases more at the ortho and para positions than at the meta position. As a result, the incoming substituents are directed to the ortho and para positions in the benzene ring.
More Questions From Class 12 Chemistry - Chapter Alcohols Phenols and Ethers
- Q:-
Explain the following with an example.
(i) Kolbe's reaction.
(ii) Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
(iii) Williamson ether synthesis.
(iv) Unsymmetrical ether.
- Q:-
How are the following conversions carried out?
(i) Propene → Propan-2-ol
(ii) Benzyl chloride → Benzyl alcohol
(iii) Ethyl magnesium chloride → Propan-1-ol.
(iv) Methyl magnesium bromide → 2-Methylpropan-2-ol.
- Q:-
Write the mechanism of acid-catalysed dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
- Q:-
Give the equations of reactions for the preparation of phenol from cumene.
- Q:-
Write equations of the following reactions:
(i) Friedel-Crafts reaction-alkylation of anisole.
(ii) Nitration of anisole.
(iii) Bromination of anisole in ethanoic acid medium.
(iv) Friedel-Craft's acetylation of anisole.
- Q:-
Explain why is ortho nitrophenol more acidic than ortho methoxyphenol?
- Q:-
Give two reactions that show the acidic nature of phenol. Compare acidity of phenol with that of ethanol.
- Q:-
Show how are the following alcohols prepared by the reaction of a suitable
Grignard reagent on methanal?
(i)

(ii)

- Q:-
Write the reactions of Williamson synthesis of 2-ethoxy-3-methylpentane starting from ethanol and 3-methylpentan-2-ol.
- Q:-
What is meant by hydroboration-oxidation reaction? Illustrate it with an example.
Popular Questions of Class 12 Chemistry
- Q:-
For the reaction R → P, the concentration of a reactant changes from 0.03 M to 0.02 M in 25 minutes. Calculate the average rate of reaction using units of time both in minutes and seconds.
- Q:-
Write the formulas for the following coordination compounds:
(i) Tetraamminediaquacobalt (III) chloride
(ii) Potassium tetracyanonickelate(II)
(iii) Tris(ethane-1,2-diamine) chromium(III) chloride
(iv) Amminebromidochloridonitrito-N-platinate(II)
(v) Dichloridobis(ethane-1,2-diamine)platinum(IV) nitrate
(vi) Iron(III) hexacyanoferrate(II)
- Q:-
(i) Write structures of different isomeric amines corresponding to the molecular formula, C4H11N
(ii) Write IUPAC names of all the isomers.
(iii) What type of isomerism is exhibited by different pairs of amines?
- Q:-
Why are solids rigid?
- Q:-
Write any two characteristics of Chemisorption.
- Q:-
Write the structures of the following compounds.
(i) α-Methoxypropionaldehyde
(ii) 3-Hydroxybutanal
(iii) 2-Hydroxycyclopentane carbaldehyde
(iv) 4-Oxopentanal
(v) Di-sec-butyl ketone
(vi) 4-Fluoroacetophenone
- Q:-
Which of the ores mentioned in Table 6.1 can be concentrated by magnetic separation method?
- Q:-
Why are pentahalides more covalent than trihalides?
- Q:-
Silver atom has completely filled d orbitals (4d10) in its ground state. How can you say that it is a transition element?
- Q:-
Glucose or sucrose are soluble in water but cyclohexane or benzene (simple six membered ring compounds) are insoluble in water. Explain.
Recently Viewed Questions of Class 12 Chemistry
- Q:-
Complete each synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or products
(i)
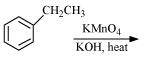
(ii)

(iii)

(iv)

(v)

(vi)
- Q:-
The molar conductivity of 0.025 mol L-1 methanoic acid is
46.1 S cm2 mol-1.
Calculate its degree of dissociation and dissociation constant. Given λ0(H+)
= 349.6 S cm2 mol-1 and λ0(HCOO-) = 54.6 S cm2 mol
- Q:-
Name two poisonous gases which can be prepared from chlorine gas.
- Q:-
The decomposition of A into product has value of k as 4.5 x 103 s-1 at 10°C and energy of activation 60 kJ mol-1. At what temperature would k be 1.5 x 104 s-1?
- Q:-
Explain
(i) The basis of similarities and differences between metallic and ionic crystals.
(ii) Ionic solids are hard and brittle.
- Q:-
The partial pressure of ethane over a solution containing 6.56 x 10-3 g of ethane is 1 bar. If the solution contains 5.00 x 10-2 g of ethane, then what shall be the partial pressure of the gas?
- Q:-
A reaction is second order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of the reactant is
(i) doubled
(ii) reduced to half?
- Q:-
While antacids and anti allergic drugs interfere with the function of histamines, why do these not interfere with the function of each other ?
- Q:-
Out of C and CO, which is a better reducing agent for ZnO ?
- Q:-
A cubic solid is made of two elements P and Q. Atoms of Q are at the corners of the cube and P at the body-centre. What is the formula of the compound? What are the coordination numbers of P and Q?
1 Comment(s) on this Question
Good explanation
- All Chapters Of Class 12 Chemistry
- All Subjects Of Class 12
