Class 12 Chemistry - Chapter Chemical Kinetics NCERT Solutions | The rate constant for the first order de
The rate constant for the first order decomposition of H2O2 is given by the following equation:
log k = 14.34 - 1.25 x 104 K/T
Calculate Ea for this reaction and at what temperature will its half-period be 256 minutes?
Arrhenius equation is given by,
k= Ae -Ea/RT
⇒In k = In A - Ea/RT
⇒In k = Log A - Ea/RT
⇒ Log k = Log A - Ea/2.303RT (i)
The given equation is
Log k = 14.34 - 1.25 104 K/T (ii)
From equation (i) and (ii), we obtain
Ea/2.303RT = 1.25 104 K/T
⇒ Ea =1.25 × 104K × 2.303 × R
= 1.25 × 104K × 2.303 × 8.314 J K - 1mol - 1
= 239339.3 J mol - 1 (approximately)
= 239.34 kJ mol - 1
Also, when t1/2= 256 minutes,
k = 0.693 / t1/2
= 0.693 / 256
= 2.707 × 10 - 3 min - 1
= 4.51 × 10 - 5s - 1
It is also given that, log k= 14.34 - 1.25 × 104K/T

= 668.95 K
= 669 K (approximately)
More Questions From Class 12 Chemistry - Chapter Chemical Kinetics
- Q:-
The half-life for radioactive decay of 14C is 5730 years. An archaeological artifact containing wood had only 80% of the 14C found in a living tree. Estimate the age of the sample.
- Q:-
For a first order reaction, show that time required for 99% completion is twice the time required for the completion of 90% of reaction.
- Q:-
The rate of a reaction quadruples when the temperature changes from 293 K to 313 K. Calculate the energy of activation of the reaction assuming that it does not change with temperature.
- Q:-
A first order reaction takes 40 min for 30% decomposition. Calculate t1/2.
- Q:-
In a reaction, 2A → Products, the concentration of A decreases from 0.5 mol L-1 to 0.4 mol L-1 in 10 minutes. Calculate the rate during this interval?
- Q:-
The conversion of molecules X to Y follows second order kinetics. If concentration of X is increased to three times how will it affect the rate of formation of Y?
- Q:-
During nuclear explosion, one of the products is 90Sr with half-life of 28.1 years. If 1μg of 90Sr was absorbed in the bones of a newly born baby instead of calcium, how much of it will remain after 10 years and 60 years if it is not lost metabolically.
- Q:-
Sucrose decomposes in acid solution into glucose and fructose according to the first order rate law, with t1/2 = 3.00 hours. What fraction of sample of sucrose remains after 8 hours?
- Q:-
For the reaction R → P, the concentration of a reactant changes from 0.03 M to 0.02 M in 25 minutes. Calculate the average rate of reaction using units of time both in minutes and seconds.
- Q:-
The decomposition of A into product has value of k as 4.5 x 103 s-1 at 10°C and energy of activation 60 kJ mol-1. At what temperature would k be 1.5 x 104 s-1?
Popular Questions of Class 12 Chemistry
- Q:-
Write the formulas for the following coordination compounds:
(i) Tetraamminediaquacobalt (III) chloride
(ii) Potassium tetracyanonickelate(II)
(iii) Tris(ethane-1,2-diamine) chromium(III) chloride
(iv) Amminebromidochloridonitrito-N-platinate(II)
(v) Dichloridobis(ethane-1,2-diamine)platinum(IV) nitrate
(vi) Iron(III) hexacyanoferrate(II)
- Q:-
(i) Write structures of different isomeric amines corresponding to the molecular formula, C4H11N
(ii) Write IUPAC names of all the isomers.
(iii) What type of isomerism is exhibited by different pairs of amines?
- Q:-
Why are solids rigid?
- Q:-
Write any two characteristics of Chemisorption.
- Q:-
Write the structures of the following compounds.
(i) α-Methoxypropionaldehyde
(ii) 3-Hydroxybutanal
(iii) 2-Hydroxycyclopentane carbaldehyde
(iv) 4-Oxopentanal
(v) Di-sec-butyl ketone
(vi) 4-Fluoroacetophenone
- Q:-
Which of the ores mentioned in Table 6.1 can be concentrated by magnetic separation method?
- Q:-
Why are pentahalides more covalent than trihalides?
- Q:-
Silver atom has completely filled d orbitals (4d10) in its ground state. How can you say that it is a transition element?
- Q:-
Glucose or sucrose are soluble in water but cyclohexane or benzene (simple six membered ring compounds) are insoluble in water. Explain.
- Q:-
Write structures of the following compounds:
(i) 2-Chloro-3-methylpentane
(ii) 1-Chloro-4-ethylcyclohexane
(iii) 4-tert. Butyl-3-iodoheptane
(iv) 1,4-Dibromobut-2-ene
(v) 1-Bromo-4-sec. butyl-2-methylbenzene
Recently Viewed Questions of Class 12 Chemistry
- Q:-
Explain briefly how +2 state becomes more and more stable in the first half of the first row transition elements with increasing atomic number?
- Q:-
Define the following terms:
(i) Mole fraction (ii) Molality (iii) Molarity (iv) Mass percentage.
- Q:-
The value of ΔfGø for formation of Cr2O3 is - 540 kJmol-1 and that of Al2 O3 is - 827 kJmol-1. Is the reduction of Cr2O3 possible with Al?
- Q:-
Aluminium crystallises in a cubic close-packed structure. Its metallic radius is 125 pm.
(i) What is the length of the side of the unit cell?
(ii) How many unit cells are there in 1.00 cm3of aluminium?
- Q:-
Use Hund's rule to derive the electronic configuration of Ce3+ ion and calculate its magnetic moment on the basis of 'spin-only' formula.
- Q:-
Sleeping pills are recommended by doctors to the patients suffering from sleeplessness but it is not advisable to take its doses without consultation with the doctor, Why?
- Q:-
What is a semiconductor? Describe the two main types of semiconductors and contrast their conduction mechanism.
- Q:-
Complete each synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or products
(i)
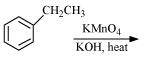
(ii)

(iii)

(iv)

(v)

(vi)
- Q:-
What makes a glass different from a solid such as quartz? Under what conditions could quartz be converted into glass?
- Q:-
Name a substance which can be used as an antiseptic as well as disinfectant.
- All Chapters Of Class 12 Chemistry
- All Subjects Of Class 12
