Question 8: Explain with examples (i) Atomic number, (ii) Mass number, (iii) Isotopes and iv) Isobars. Give any two uses of isotopes.
Answer:
(I) Atomic number: The atomic number of a component is equivalent to the quantity of protons in the nucleus of its molecule.
e.g., Oxygen has 6 protons thus atomic no. = 6.
(ii) Mass number: The mass number of a molecule is equivalent to the quantity of protons and neutrons in its nucleus.
Nucleons = number of protons + number of neutrons
Example: Protons + Neutrons = Nucleus = Mass number = 6 + 6 = 12
(iii) Isotopes: Isotopes are molecules of a similar component which have different mass numbers however same atomic number.
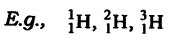
(iv) Isobars: Isobars are molecules having similar mass number however different atomic numbers.
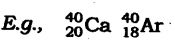
Both calcium and argon have a similar mass number yet unique atomic number.
Two uses of isotopes are:
(I) An isotope of iodine is utilized in the treatment of goiter.
(ii) An isotope of uranium is utilized as a fuel in atomic reactors.



Add Comment