Class 12 Chemistry - Chapter Solutions NCERT Solutions | Calculate the mass of ascorbic acid (Vit
Calculate the mass of ascorbic acid (Vitamin C, C6H8O6) to be dissolved in 75 g of acetic acid to lower its melting point by 1.5°C. Kf= 3.9 K kg mol-1.
Mass of acetic acid, w1= 75 g Molar mass of ascorbic acid (C6H8O6),
M2= 6 × 12 + 8 × 1 + 6 × 16
= 176 g mol - 1
Lowering of melting point, ΔTf = 1.5 K
We know that:

= (1.5 x 176 x 75) / (3.9 x 1000)
= 5.08 g (approx)
Hence, 5.08 g of ascorbic acid is needed to be dissolved.
More Questions From Class 12 Chemistry - Chapter Solutions
- Q:-
A 5% solution (by mass) of cane sugar in water has freezing point of 271 K. Calculate the freezing point of 5% glucose in water if freezing point of pure water is 273.15 K.
- Q:-
A solution of glucose in water is labelled as 10% w/w, what would be the molality and mole fraction of each component in the solution? If the density of solution is 1.2 g mL-1, then what shall be the molarity of the solution?
- Q:-
Henry's law constant for CO2 in water is 1.67 x 108Pa at 298 K. Calculate the quantity of CO2in 500 mL of soda water when packed under 2.5 atm CO2 pressure at 298 K.
- Q:-
Calculate the mass of a non-volatile solute (molar mass 40 g mol-1) which should be dissolved in 114 g octane to reduce its vapour pressure to 80%.
- Q:-
The vapour pressure of pure liquids A and B are 450 and 700 mm Hg respectively, at 350 K. Find out the composition of the liquid mixture if total vapour pressure is 600 mm Hg. Also find the composition of the vapour phase.
- Q:-
Calculate the mole fraction of benzene in solution containing 30% by mass in carbon tetrachloride.
- Q:-
How many mL of 0.1 M HCl are required to react completely with 1 g mixture of Na2CO3 and NaHCO3 containing equimolar amounts of both?
- Q:-
H2S, a toxic gas with rotten egg like smell, is used for the qualitative analysis. If the solubility of H2S in water at STP is 0.195 m, calculate Henry's law constant.
- Q:-
Boiling point of water at 750 mm Hg is 99.63°C. How much sucrose is to be added to 500 g of water such that it boils at 100°C.Molal elevation constant for water is 0.52 K kg mol-1.
- Q:-
An aqueous solution of 2% non-volatile solute exerts a pressure of 1.004 bar at the normal boiling point of the solvent. What is the molar mass of the solute?
Popular Questions of Class 12 Chemistry
- Q:-
For the reaction R → P, the concentration of a reactant changes from 0.03 M to 0.02 M in 25 minutes. Calculate the average rate of reaction using units of time both in minutes and seconds.
- Q:-
Write the formulas for the following coordination compounds:
(i) Tetraamminediaquacobalt (III) chloride
(ii) Potassium tetracyanonickelate(II)
(iii) Tris(ethane-1,2-diamine) chromium(III) chloride
(iv) Amminebromidochloridonitrito-N-platinate(II)
(v) Dichloridobis(ethane-1,2-diamine)platinum(IV) nitrate
(vi) Iron(III) hexacyanoferrate(II)
- Q:-
(i) Write structures of different isomeric amines corresponding to the molecular formula, C4H11N
(ii) Write IUPAC names of all the isomers.
(iii) What type of isomerism is exhibited by different pairs of amines?
- Q:-
Why are solids rigid?
- Q:-
Write any two characteristics of Chemisorption.
- Q:-
Write the structures of the following compounds.
(i) α-Methoxypropionaldehyde
(ii) 3-Hydroxybutanal
(iii) 2-Hydroxycyclopentane carbaldehyde
(iv) 4-Oxopentanal
(v) Di-sec-butyl ketone
(vi) 4-Fluoroacetophenone
- Q:-
Which of the ores mentioned in Table 6.1 can be concentrated by magnetic separation method?
- Q:-
Why are pentahalides more covalent than trihalides?
- Q:-
Silver atom has completely filled d orbitals (4d10) in its ground state. How can you say that it is a transition element?
- Q:-
Glucose or sucrose are soluble in water but cyclohexane or benzene (simple six membered ring compounds) are insoluble in water. Explain.
Recently Viewed Questions of Class 12 Chemistry
- Q:-
How the following conversions can be carried out?
(i) Propene to propan-1-ol
(ii) Ethanol to but-1-yne
(iii) 1-Bromopropane to 2-bromopropane
(iv) Toluene to benzyl alcohol
(v) Benzene to 4-bromonitrobenzene
(vi) Benzyl alcohol to 2-phenylethanoic acid
(vii) Ethanol to propanenitrile
(viii) Aniline to chlorobenzene
(ix) 2-Chlorobutane to 3, 4-dimethylhexane
(x) 2-Methyl-1-propene to 2-chloro-2-methylpropane
(xi) Ethyl chloride to propanoic acid
(xii) But-1-ene to n-butyliodide
(xiii) 2-Chloropropane to 1-propanol
(xiv) Isopropyl alcohol to iodoform
(xv) Chlorobenzene to p-nitrophenol
(xvi) 2-Bromopropane to 1-bromopropane
(xvii) Chloroethane to butane
(xviii) Benzene to diphenyl
(xix) tert-Butyl bromide to isobutyl bromide
(xx) Aniline to phenylisocyanide
- Q:-
Give the uses of freon 12, DDT, carbon tetrachloride and iodoform.
- Q:-
Give the oxidation state, d-orbital occupation and coordination number of the central metal ion in the following complexes:
(i) K3[Co(C2O4)3]
(ii) cis-[Cr(en)2Cl2]Cl
(iii) (NH4)2[CoF4]
(iv) [Mn(H2O)6]SO4
- Q:-
The half-life for radioactive decay of 14C is 5730 years. An archaeological artifact containing wood had only 80% of the 14C found in a living tree. Estimate the age of the sample.
- Q:-
Show how each of the following compounds can be converted to benzoic acid.
(i) Ethylbenzene (ii) Acetophenone
(iii) Bromobenzene (iv) Phenylethene (Styrene)
- Q:-
Show how will you synthesize:
(i) 1-phenylethanol from a suitable alkene.
(ii) cyclohexylmethanol using an alkyl halide by an SN2 reaction.
(iii) pentan-1-ol using a suitable alkyl halide?
- Q:-
What type of defect can arise when a solid is heated? Which physical property is affected by it and in what way?
- Q:-
What is meant by 'disproportionation'? Give two examples of disproportionation reaction in aqueous solution.
- Q:-
Complete each synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or products
(i)
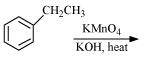
(ii)

(iii)

(iv)

(v)

(vi)
- Q:-
Predict all the alkenes that would be formed by dehydrohalogenation of the following halides with sodium ethoxide in ethanol and identify the major alkene:
(i) 1-Bromo-1-methylcyclohexane
(ii) 2-Chloro-2-methylbutane
(iii) 2,2,3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane.
2 Comment(s) on this Question
Vfvdhvs
To is in °C in question.
- All Chapters Of Class 12 Chemistry
- All Subjects Of Class 12
